10 Microservice best practices for your projects
The 80/20 rule is all about focusing on the important things while ignoring everything else. The same may be applied to microservices deployments, which we’ll discuss further down.
1. Improve productivity with Domain-Driven Design(DDD)
Microservices, ideally, should be designed around business capabilities using DDD. It enables high-level functionality coherence and provides loosely coupled services.
There are two phases to every DDD model: strategic and tactical. The strategic phase ensures that design architecture encapsulates business capabilities. The tactical phase, on the other hand, allows the creation of a domain model using different design patterns.
Entities, aggregates, and domain services are some of the design patterns that might help you design loosely coupled microservices.
Learn how SoundCloud reduced release cycle time with DDD.
SoundCloud’s service architecture followed the Backend for frontend(BFF) pattern. There were, however, complications and concerns with duplicate codes. Furthermore, they used the BFF pattern for the business and authorization logic in the BFF pattern, which was risky.
As a result, they decided to use a Domain-driven design pattern and develop a new approach known as “Value Added Services (VAS).”
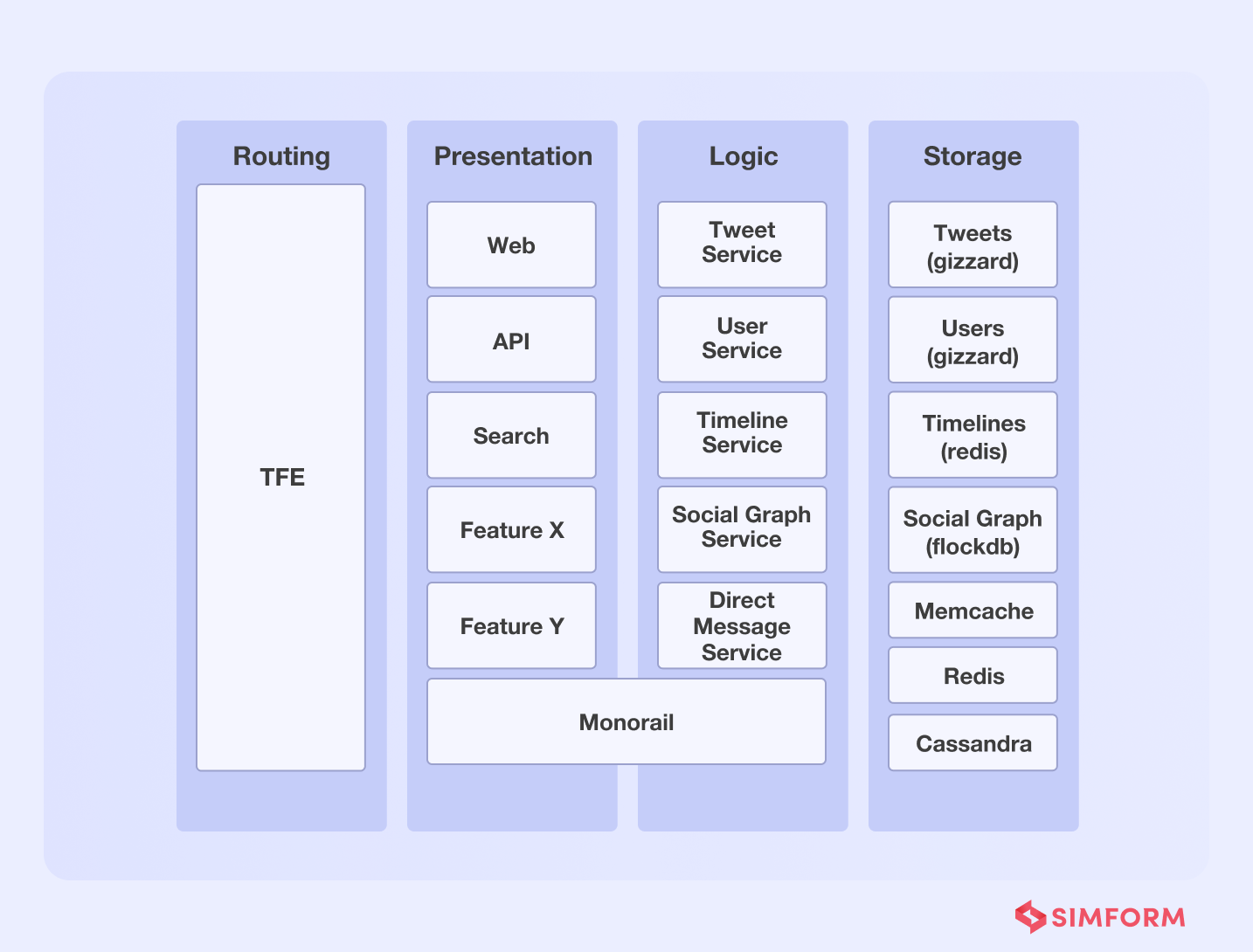
There are three service tiers in VAS. The first one is the Edge layer, which functions as an API gateway. The value-added layer is the second, which processes data from different services to provide a rich user experience. Lastly, the “Foundation,” which provides the domain’s building blocks, is the third layer.
Within the DDD pattern, SoundCloud employs VAS as an aggregate. VAS also enables the separation of concerns and provides a centralized orchestration. It can execute authorization and orchestrate calls to associated services for metadata synthesis.
Using the VAS approach, SoundCloud managed to decrease release cycles while improving team autonomy.
2. Have quicker responses with the Single Responsibility Principle (SRP)
SRP is a microservice design principle in which each module or class is required to do one thing assigned well enough for enhanced functionality. Each service or function has its own set of business logic that is specific to the task at hand.
One of the major benefits of SRP is reduced dependencies. There is no overhead on any service because each function is designed to perform specific tasks. It also reduces the response time by eliminating the need for a service to wait for support services to execute before responding to a user request.
Example of how Gojek achieved higher reliability and lower response time using SRP
Gojekis an on-demand marketplace that connects motorcycle drivers and riders. One distinct feature is a chat capability that allows users to engage with drivers via the “Icebreaker” application.
The Icebreaker’s heavy reliance on services to build a communication channel between users and drivers was a hurdle for Gojek. To create a channel, for example, the icebreaker will need to perform tasks like,
- Authorize API calls
- Fetch customer’s profile
- Fetch driver’s details
- Verify whether the customer-driver profile matches the active order details
- Create a communication channel
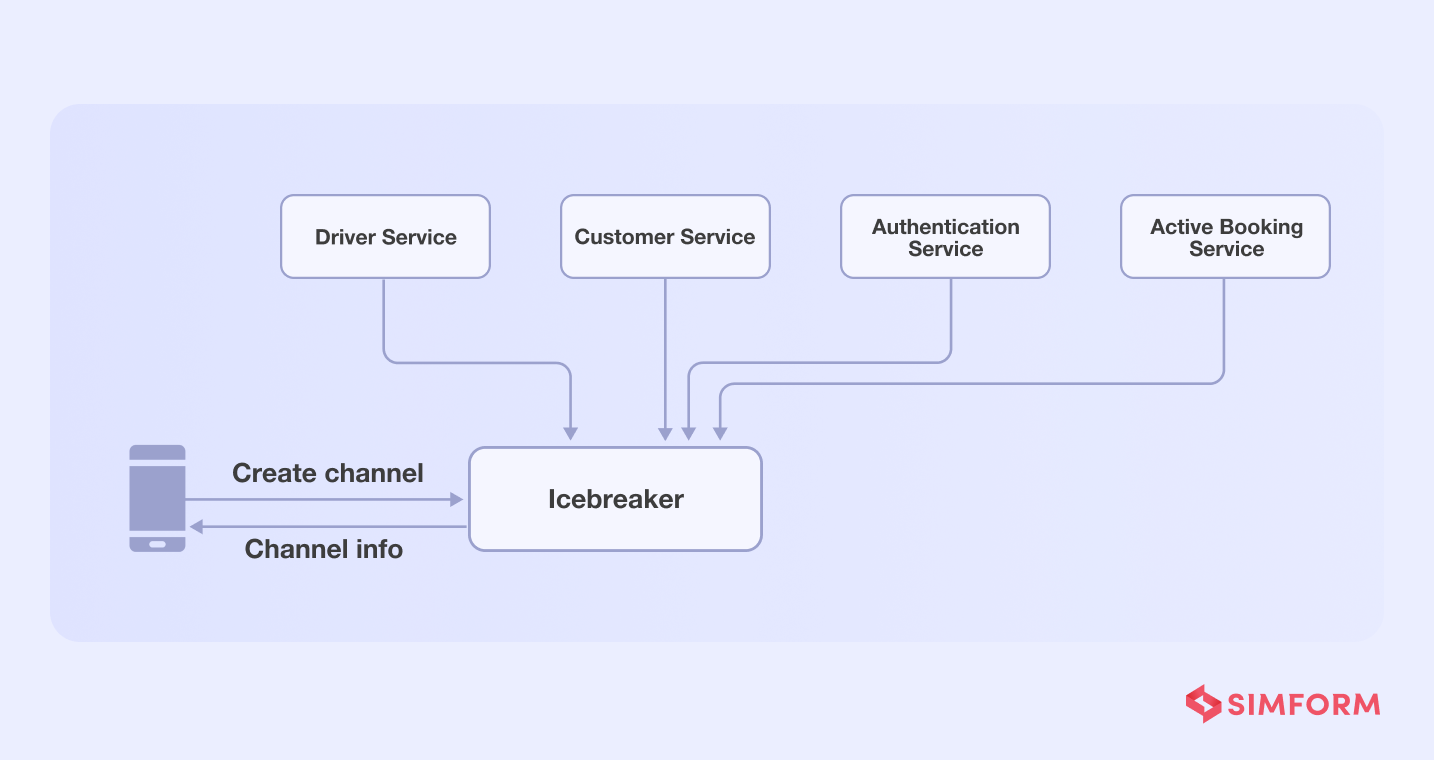
The problem with dependency on several functions/services is that if one of them fails, the entire chat function will fail.
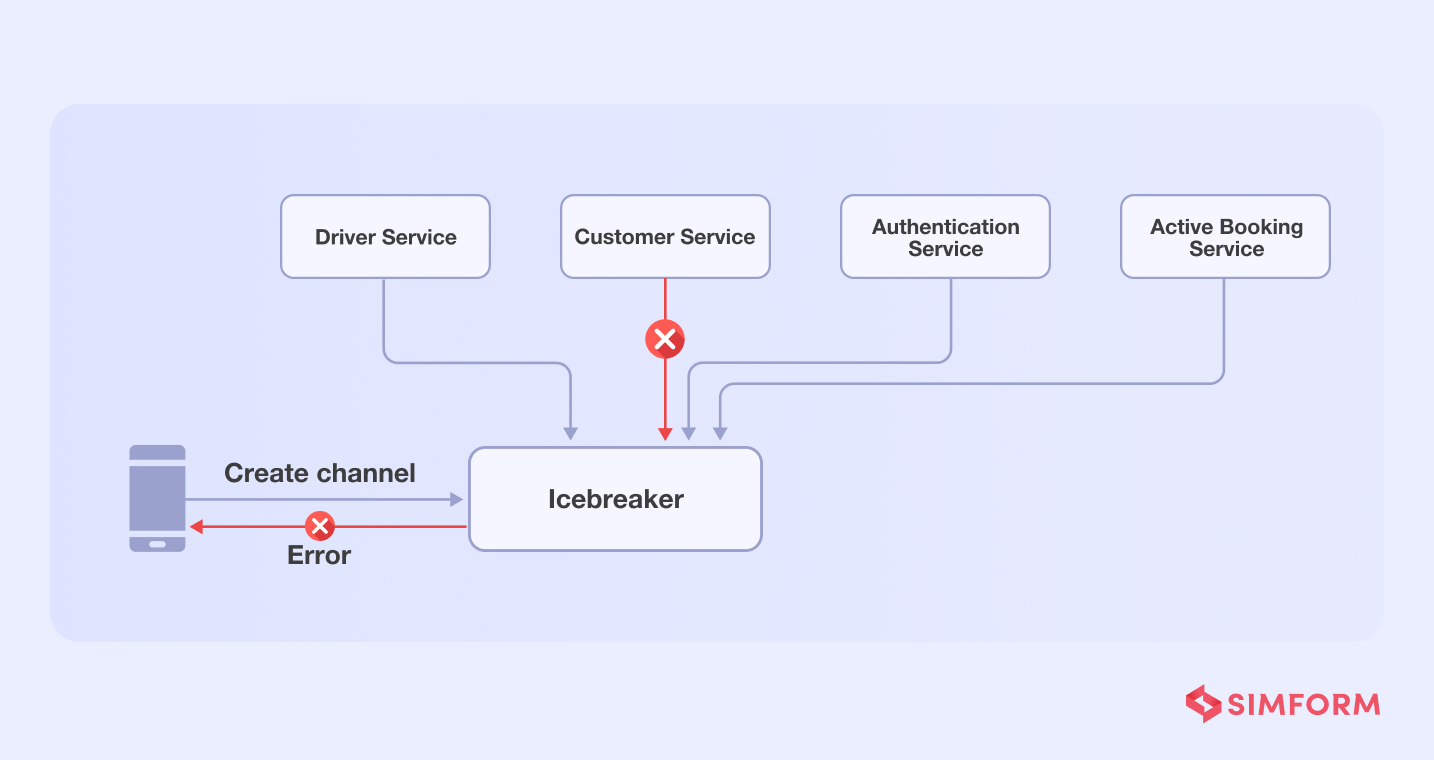
Gojek teams applied the single responsibility principle to addd services for each function, assigning tasks to each and reducing the load on a single service.
- API call function- They added Kong API gateway for authentication functionality
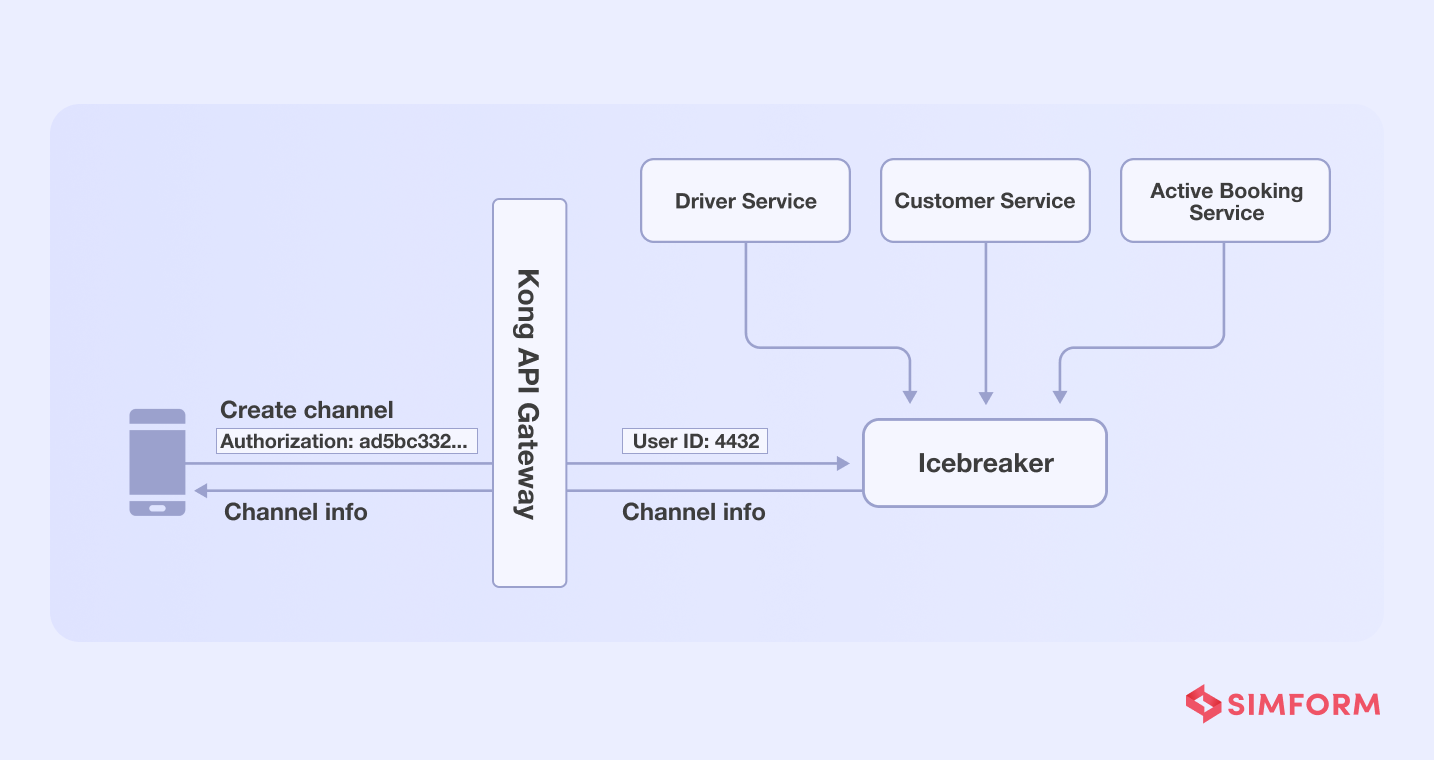
- Profile retrieval-Icebreaker needed chat tokens from driver’s and user’s data stored in separate databases, which were then stored in the Icebreaker’s data store. As a result, there was no need to perform any further retrieval in order to create the channel.
- Active booking- Icebreaker needed to verify whether an active booking had already been made when a user hits the channel creation API. The Gojek team used the worker-server approach to reduce this dependency.
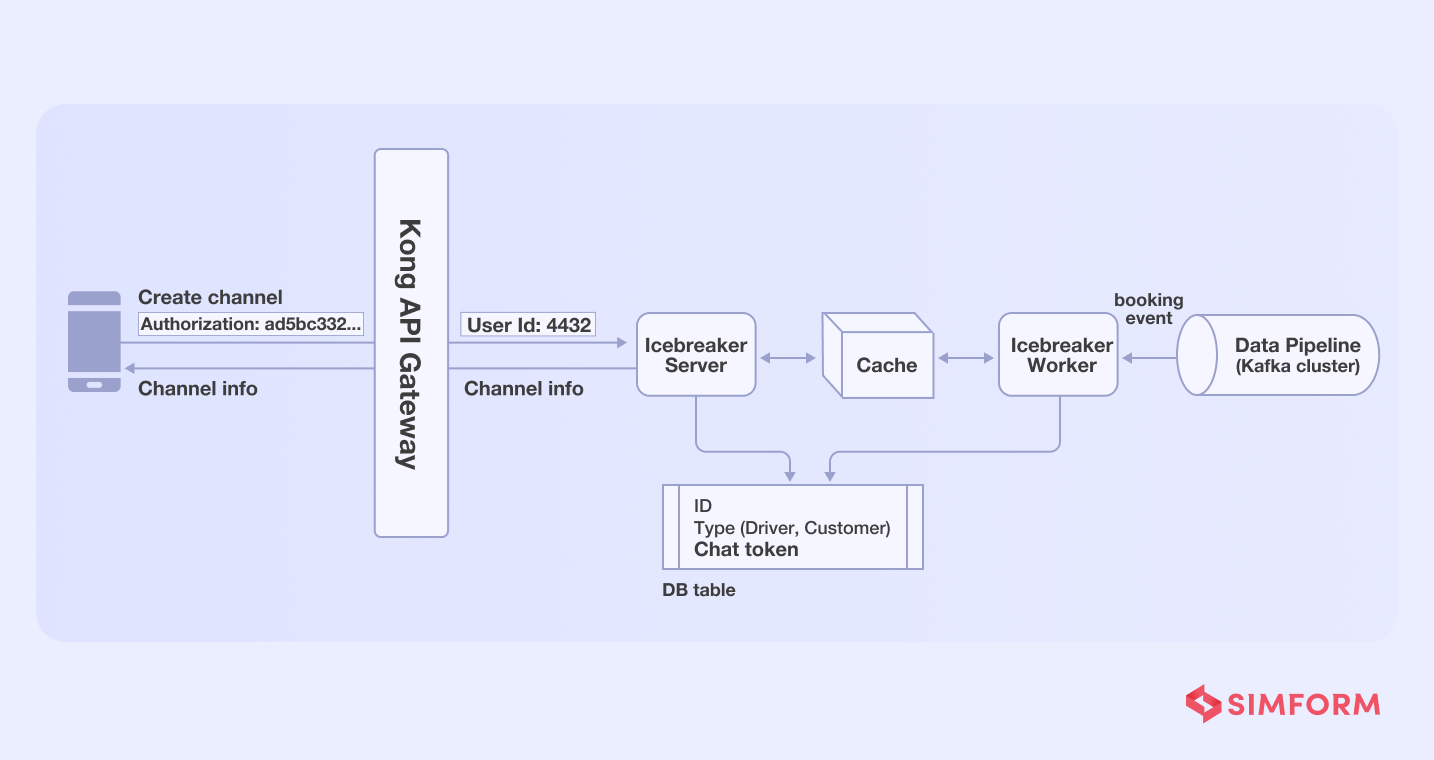
So, each time an order is placed, a worker creates a communication channel and stores it in the Redis cache, which a server pushes as per need each time a user hits the channel API.
As a result, Gojek reduced its response time by 95% with the single principle responsibility approach.
3. Enable service autonomy with independent microservices
Independent microservice is a practice of taking the service isolation to a step further. Through independent microservice practices, three forms of independence can be obtained.
- Independent service evolution is a process of isolating feature development based on the need for evolution.
- Independent testing is a process of conducting tests that prioritize and focuses on the service evolution. This decreases the number of test failures caused by service dependencies.
- Independent deployment reduces the chances of downtime due to service upgrades.. It is beneficial, especially if you have a cyclic dependency during the app’s deployment.
Amazon’s single-purpose functions and independent microservices’ management issues
Back in 2001, developers at Amazon found it difficult to maintain a deployment pipeline with a monolithic architecture. So, they chose to migrate to a microservice architecture, but the real challenge began after the migration.
Amazon teams pulled single-purpose units and wrapped them with a web interface. It was undoubtedly an efficient solution, but the difficulty in managing several single-purpose functions was the issue.
Merging the services them week after week for deployment became a massive challenge as the services increased. Hence, development teams at Amazon built “Apollo,” an automated deployment system based on the decoupled services.
Further, they established a rule that all-purpose functions must communicate through a web interface API. They defined a set of decoupling rules that every function needs to follow.
Lastly, they had to deal with manual handoffs, which resulted in “deadtime.” Eventually, the deployment pipeline sequence was discovered to reduce manual handoffs for improved efficiency of the entire system.
4. Embrace parallelism with asynchronous communications
Without proper communication between services, the performance of your microservices can suffer severely. There are two communication protocols popularly used for microservices,
- Synchronous communication is a blocking-type communication protocol where microservices form a chain of requests. Though it has a single point of failure and it lags in performance due to higher dependency and
- Asynchronous communication is a non-blocking protocol that follows event-driven architecture. It allows parallel execution of requests and provides better resilience.
The asynchronous communication protocol is the better option for enhanced communication between microservices. It reduces the coupling between services during the execution of user requests.
How Flywheel Sports powered real-time broadcast with enhanced microservice communication?
Flywheel Sports was launching “FlyAnywhere,” a platform for their fitness community that enhanced the bike riding experience through real-time broadcast. Flywheel’s engineers built the platform using a modular approach and microservice architecture.
It did, however, have communication challenges, which resulted in network failures and system availability issues. To solve these issues, they created a checklist of features like,
- Service discovery
- Messaging
- Queuing
- Logging
- Load balancing
They built “Hydra,” an internal library that supports the above features and Redis clusters. They tied each microservice to a shared Redis cluster and used pub/sub (asynchronous communications) to maintain inter-process communication.
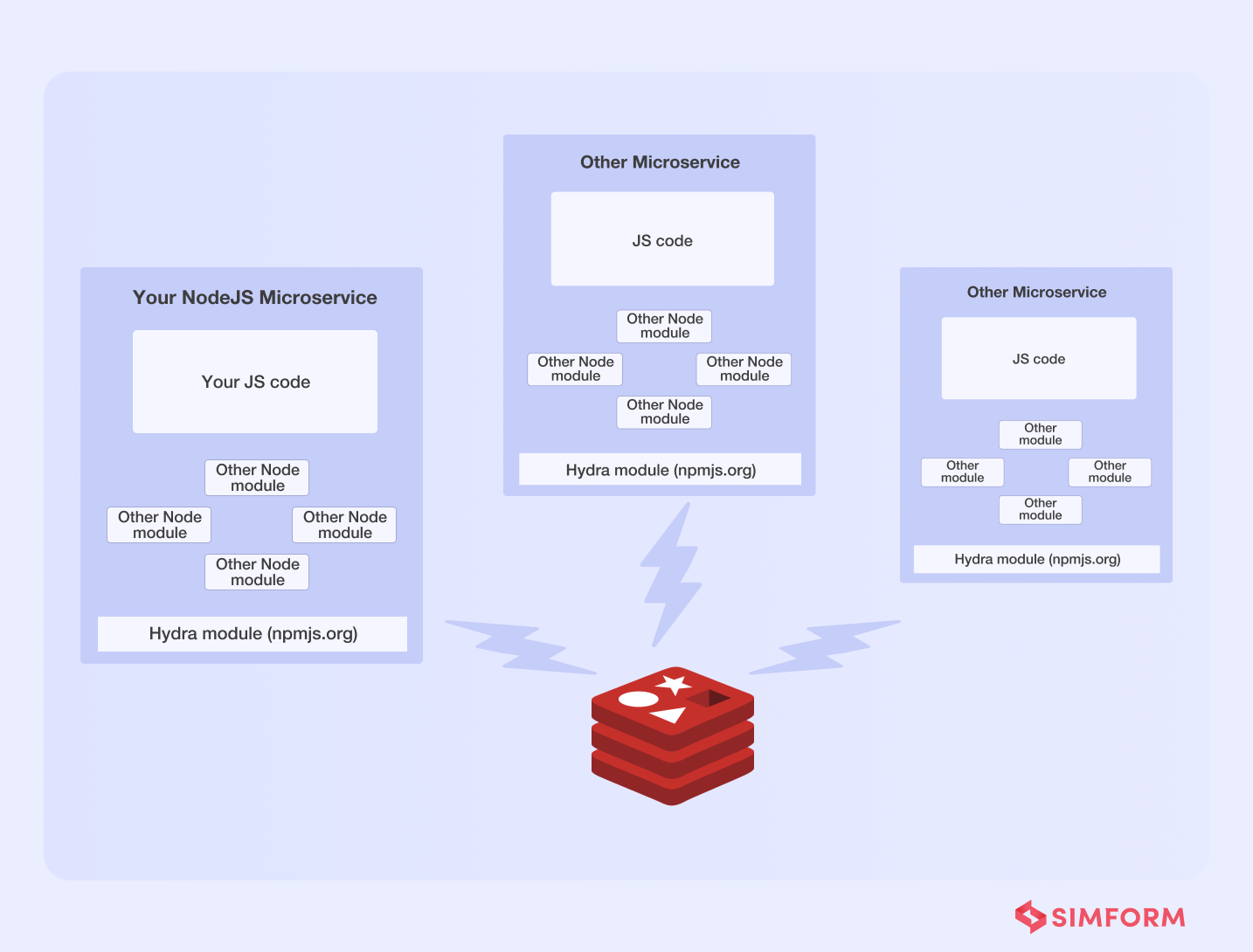
Not just that, Hydra also assisted them in mitigating the single dependency issues of microservices by enabling features like,
- Inter-service communication
- Service discovery
- Load balancing and routing
- Self-registration of services with zero configuration
- Job queues
Overall, we can conclude that asynchronous communication assisted Flywheel in establishing a solid foundation for providing real-time broadcasts to its FlyAnywhere consumers via Hydra.
5. Separate microservice database to reduce latency
Although microservices are loosely coupled, they all require to retrieve data from the same datastore with a shared database. In such instances, the database must deal with multiple data queries and latency issues. The solution might be a distributed database for microservices, with each service having a data store of its own can be the answer.
A separate microservice database allows services to store the data locally in a cache. Latency is reduced as a result of this. Because there is no single point of failure with a distinct data store, security and resilience are also improved.
Twitter’s ability to process millions of QPS was improved through a dedicated microservice datastore.
Twitter migrated from monolithic software architecture to a microservices architecture in 2012. It utilized multiple different services, including Redis and Cassandra, to handle about 600 requests per second. However, as the platform scaled, it needed a database solution that was scalable, resilient, and capable of handling more queries per second.
Initially, Twitter was built on MySQL and was further moved from a small database instance to a large one. This led to the creation of large database clusters, because of which moving data across instances was a time-consuming effort.
As a solution to this problem, Twitter incorporated several changes. One of which is the introduction of Gizzard, a framework that helped them create distributed datastores. It works as a middleware networking service and handles failures.
Further, Twitter added Cassandra as a data storage solution. Though Gizzard and Cassandra helped Twitter handle data queries, the latency problem persisted. They needed millions of queries per second with low latency in a real-time environment.
So, they created an in-house distributed database called ‘Manhattan” to improve latency and handle several queries per second. Twitter improved reliability, availability, and latency, among other things, with this distributed system. Furthermore, Twitter migrated data from MySQL to Manhattan and adopted additional storage engines to server different traffic patterns.
Another key aspect of Twitter’s dedicated database solution was the use of Twemcache and Redis. It helped them protect backing data stores from heavy read traffic.
A dedicated microservice datastore approach helped Twitter handle,
- More than 20 production clusters
- More than 1000 databases
- Manage tens of thousands of nodes
- Handle tens of millions of queries per asecond(QPS)
6. Containerize microservices to improve process efficiency
Containerization of microservices is one of the most efficient best practices. Containers allow you to package the bare minimum of program configurations, libraries, and binaries. As a result, it is lightweight and portable across environments.
Apart from this, containers share the kernel and operating system, which reduces the need for resources needed for the individual OS. There are many benefits that containerization can provide,
- Isolation of process with minimal resources
- Smaller memory footprint
- Higher data consistency due to shared OS.
- No impact of sudden changes of outside environment on containers
- Optimized costs and quicker iterations
- Rapid rollouts and rollbacks
Learn how Spotify migrated 150 services to Kubernetes to process 10 million QPS.
Spotify has been containerizing microservices since 2014; however, by 2017, they understood that their home-grown orchestration system, Helios, was insufficient to iterate quickly for 200 autonomous production teams.
Kubernetes for Spotify was the solution to Helios’ inefficiency. To avoid putting all of their eggs in one basket, Spotify engineers migrated some services to Kubernetes, which runs alongside Helios.
They used Kubernetes APIs and extensibility features for integration after a thorough investigation of core technical challenges. Further, Spotify accelerated the migration to Kubernetes in 2019, focusing on stateless services. They migrated over 150 services in order to handle 10 million requests per asecond.
7. Increase native UI capabilities with micro frontend
Micro frontend architecture is a method of breaking down a monolithic frontend into smaller elements. It follows the microservice architecture and enables individual UI element upgrades. With this approach, you can make changes to individual components and test and deploy them.
Further, micro frontend architecture also helps in creating native experiences. For example, it enables the usage of simple browser events for communication that are easier to maintain than APIs. Micro frontends improve CI/CD pipelines by enabling faster feedback loops. So, you can build a frontend that is both scalable and agile.
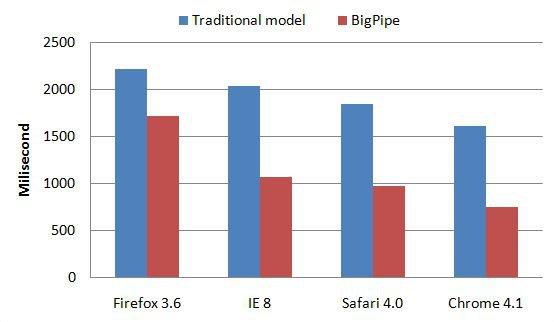
How Facebook improved web page latencies with BigPipe
In 2009, Facebook was having trouble with the frontend of its website and wanted a solution to reduce loading times. The traditional front-end architecture needed overlapping browser rendering and page generation optimizations. Such optimizations were the only solution to help them in reducing the latency and response time.
Which is why Facebook built a micro frontend solution called the BigPipe. This allowed Facebook to break the web page into smaller components called “pagelets.” Using BigPipe, Facebook has improved latency across browsers’ web pages.
Over time, modern micro front-end architectures have evolved from web pages to support use cases like web apps and mobile applications as awell.
8. Secure microservices for data protection
Microservices communicate with external services or platforms through APIs, and securing such communication is essential. Data can be compromised, and hackers can take control of core services and disrupt your app’s operations if you don’t use effective precautions. To give you a perspective, data breaches cost businesses more than $2.9 million every minute.
So, microservices security is critical to your business. There are many ways to secure microservices like,
- SSL/TLS encryptions
- Multi-factor authentications
- Restricted data access
- Web application firewalls
- Vulnerability scanning
- Penetration testing
OFX secured microservices with a middle-tier security tool
OFX is an Australian international financial transfer institution that processes more than $22 billion worth of transactions every year.
After migration to the cloud environment, OFX needed a highly secure solution to increase visibility and protection against cyber threats defined by the Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP).
OFX partners and external services communicate with the microservices through APIs in an internal network. Therefore, they needed to improve security and visibility to properly verify access requests from external platforms.
To tackle this, OFX deployed a security tool in the mid-tier environment with an agent on their web servers to have visibility of several aspects, including,
- Detection of suspicious patterns
- Monitoring of login attempts
- Blocking malicious traffic
- Extensive penetration testing
By adding a security tool in the middle-tier, security teams and cloud architects can track every interaction of APIs. It helped them detect anomalies and secure amicroservices.
9. Simplify parallel programming with immutable APIs
Microservices and immutability both share the idea of parallelism, which also helps in applying the Pareto Principle. In addition, parallelism allows you to accomplish more within less time.
Immutability is a concept where data or objects, once created, are not modified. Therefore, parallel programming is much easier, especially when using microservice architecture.
Understanding how immutable containers improve security, latency, and more.
Let’s consider a use case like an eCommerce web app that needs integration of external payment gateways and third-party services.
Integration of external services needs APIs for microservice communication and data exchange. Traditionally APIs are mutable and provide the power of creating several mutations as per need.
However, the problem with mutable APIs is susceptibility to cyber-attacks. Hackers exploit shell data access to inject malicious codes.
On the other hand, immutability with containerized microservices improves security and data integrity. You can simply remove the faulty containers with immutable containers instead of fixing them or upgrading them. In other words, immutable APIs can help your eCommerce platform secure users’ data.
Another key advantage of immutable API is parallel programming. A major caveat of concurrent programs is how changes in one thread impact other threads. It leads to complications for programmers who need to figure out the context in which their thread executes.
Immutable APIs solve this problem by restricting the side effects of one thread on others. It restricts the change of state no matter which version of an object a thread accesses. If a thread needs an altered version of an object, a new one is created in parallel. So, you can execute multiple threads in parallel, improving programming aefficiency.
10. Increase delivery speeds with a DevOps culture
DevOps is a set of practices that breaks the siloed operational and development capabilities for enhanced interoperability. Adopting DevOps can help your organization with a cohesive strategy and efficient collaboration, among other benefits.
DocuSign reduced errors and improved CI/CD efficiency with DevOps.
DocuSign introduced the e-signing technology using the Agile approach for software development. However, they soon realized that the lack of collaboration between individual teams resulted in failures.
DocuSign’s business model, which involved contracts and signatures, needed continuous integration. In addition, the exchange of signatures and approvals needs to be error-free, as a single misattribution can lead to severe problems.
So, DocuSign adopted the DevOps culture to improve collaboration between operation and development team members. Despite the cultural shift in the organization due to DevOPs adoption, the CI/CD problem persisted. They used application mock for internal APIs to support continuous integration.
The application mock tool offers a mock endpoint and response. DocuSign combines it with incident management and tests the app before release through simulations. It helped them quickly build, test and release applications through a cohesive strategy.
Simulations allowed them to test the app’s behavior in real-life scenarios, improve fault isolation and make quick changes. So, they could continuously test, integrate changes, and have continuous delivery cohesively.
80/20 the Simform way!
The 80/20 principle is all about reducing efforts and maximize gains. These microservice best practices can help you achieve maximum gains. However, which one to choose remains use case specific. Take an example of CrayPay, that needed an m-payment solution for retail payments.
Si
This awesome post is was made by : https://www.simform.com/author/hiren-simform/
